Abstract
Background: Bortezomib has efficacy in follicular lymphoma (FL). Though generally well tolerated, it is associated with a few known toxicities, including neurotoxicity. As a chronically administered agent, it is important to investigate the tolerability of bortezomib over time as a single agent and in combination with chemotherapy. The current method of summarizing adverse events (AEs) -focusing on the maximum grade and reporting only grade 3 or higher incidences- fails to capture toxicity that evolves over time or chronic low grade AEs that may occur at significant expense to patients' quality of life. In this study, we applied the Toxicity over Time (ToxT) analytic approach (Thanarajasingam et al, Lancet Oncol 2016), which graphically and analytically depicts AEs longitudinally, to a randomized Phase 2 ECOG-ACRIN sponsored study, E2408, to characterize chronic toxicity of bortezomib (V) when added to standard bendamustine-rituximab (BR) induction in previously untreated high risk FL.
Methods: In E2408, patients (pts) were randomized to one of 3 arms at a 1:2:2 ratio: A) BR x 6 followed by maintenance rituximab (MR) x 2 years (yrs) vs B) BVR x 6 (bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 IV/SQ days 1, 4, 8, 11) then MR x 2 yrs vs C) BR x 6 then MR x 2 yrs + lenalidomide 20mg/day x 1 yr. Pts enrolled 1/2011-5/2015. This analysis focuses on the 6 cycles of induction only, with arms A and C combined. Six AEs of interests were selected, 4 symptomatic (subjective) AEs (peripheral sensory neuropathy (PSN), diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, fatigue); and 2 non-symptomatic (objective) AEs (neutropenia and thrombocytopenia). Treatment-related post baseline AEs of any grade were investigated by conventional maximum grade toxicity analysis (ToxC) and ToxT methods. The mean AE grades over cycles were analyzed by repeated measures models, time to grade 2 or higher (gr2+)AE were analyzed with time-to-event analysis; and AE profile over the entire course of the study was summarized by area under the curve (AUC) analyses. Comparisons were performed between treatment arms (BVR vs. BR).
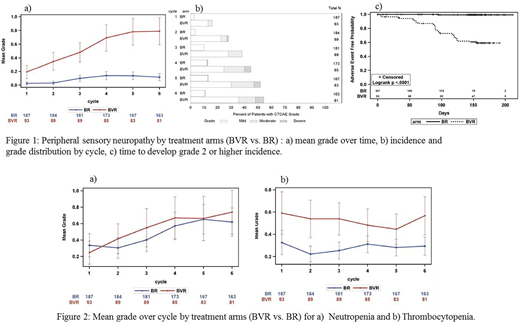
Results: All 280 randomized treated pts (187 on BR, 93 on BVR) were included in the analysis regardless of eligibility status; 87% (163/187 BR, 81/93 BVR) completed all 6 cycles. Analyzing the symptomatic AEs,ToxC indicates that the overall incidence of grade 3+ PSN was significantly higher in BVR (12%) than BR (1%) (p<.0001). Additional, ToxT captures the trajectory, demonstrating a rapid, rising incidence and worsening grade of PSN on BVR vs BR over 6 cycles in a steam plot of mean gr. by cycle (Fig 1a) and bar chart of incidence and grade per cycle (c1: 13% gr1 3% gr2, c6: 36% gr1 12% gr2 6% gr3 on BVR; c1: 3% gr1, c6: 10% gr1 1% gr2 on BR, Fig. 1b). Risk of developing gr2+ PSN was significantly higher in BVR than BR with 28% vs 0.5% by day 100 (HR=0.01, p<.0001, Fig. 1c). ToxC captures a higher incidence of grade 3+ diarrhea on BVR (7% vs. 1% , p=.01) while AUC from ToxT includes chronic lower grade diarrhea, that is substantial over time on BVR vs. BR (p<.0001), but is not cumulative. Furthermore, the risk of developing gr2+ diarrhea affecting drug tolerability is significantly higher on BVR than BR(13% vs 5% by day 100) (HR=0.3, p=.05). Febrile neutropenia appeared to be similar, and fatigue was marginally more severe under BVR (p=.06 by AUC). For objective AEs, ToxC reveals no significant difference in neutropenia or thrombocytopenia BVR vs BR (neutropenia gr 3+: 36% vs 31%, p=.4; thrombocytopenia gr3+: 10% vs. 5%, p=.12). However, ToxT illustrates that neutropenia is cumulative, worsening over repeated exposure to drug (c1: 2% gr1 5% gr2 5% gr 3+ , c6: 7% gr1 10% gr2 12% gr3+ both arms combined; p<.0001) on mean grade over time (Fig. 2a). In contrast, thrombocytopenia does not worsen with continued treatment (Fig 2b, p=.73).
Conclusions: Compared with conventional toxicity analysis (ToxC), ToxT delineated important additional and clinically relevant depictions of both symptomatic and laboratory AEs over time for bortezomib added to BR in FL pts. In patients receiving BVR, close monitoring is suggested for PSN, diarrhea and neutropenia for reassessment of risks and benefits, symptom interventions and dose modification. Longitudinal toxicity analyses such as ToxT can guide AE interventions as well as patient and clinician education, and provide a more patient-centered toxicity assessment of chronically administered therapies for lymphoma.
Hong:Merck: Consultancy. Evens:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Tesaro: Research Funding; Affimed: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics International DMC: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Advani:Kura: Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Kyowa: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Cell Medica: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Infinity: Research Funding; Gilead/Kite: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Janssen: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Regeneron: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board, Research Funding; Forty Seven Inc.: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Millenium: Research Funding; Agensys: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Autolus: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board. Gascoyne:NanoString: Patents & Royalties: Named Inventor on a patent licensed to NanoString Technologies. Witzig:Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Dueck:Bayer: Employment; Pfizer: Honoraria; Phytogine: Employment. Kahl:Genentech: Consultancy; Acerta: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Juno: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; CTI: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal